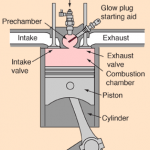
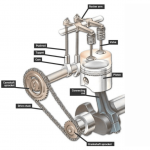
A standard internal combustion engine features either diesel or gas as its source of fuel. The two vary mainly in their ideal applications and the ways in which they function, which ultimately influences their life expectancy. In this article, you will learn about gas and diesel engine operation, maintenance and repair considerations, and finally diesel vs gas life expectancy.
Diesel vs. Gas Engine Operation
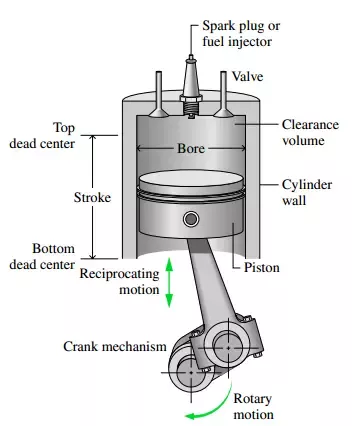
Diesel and gas engines are both internal combustion engines. Through a series of chemical processes including combustion, the engines produce kinetic energy. For both types of engines, fuel in the piston cylinder assembly combines with air and combusts. The internal combustion inside the piston-cylinder assembly forces the piston up and down and in turn, creates rotary motion in the crank shaft to which the pistons attach. Through the proper timing, all the cylinders create seamless rotary motion.
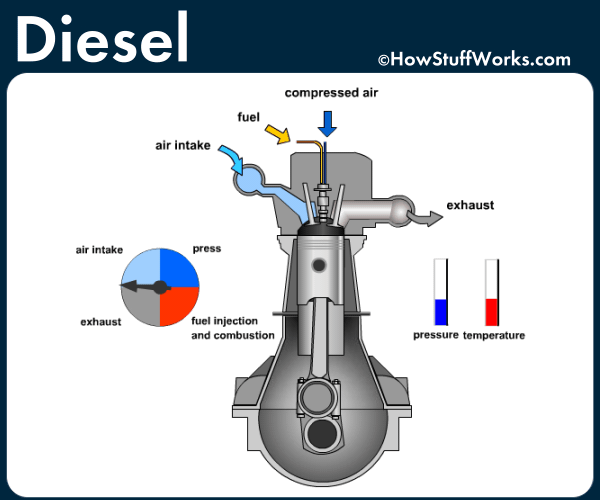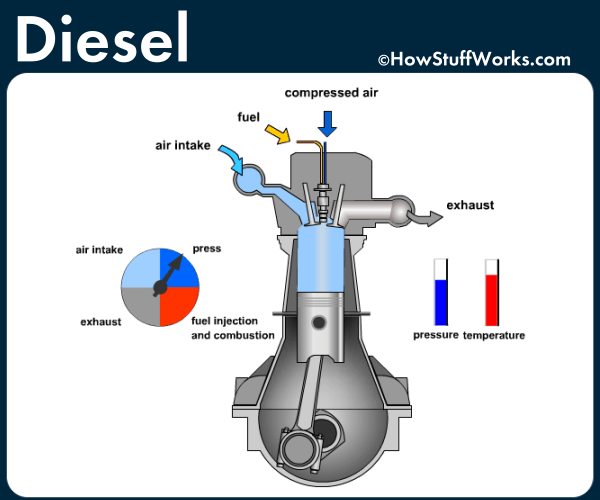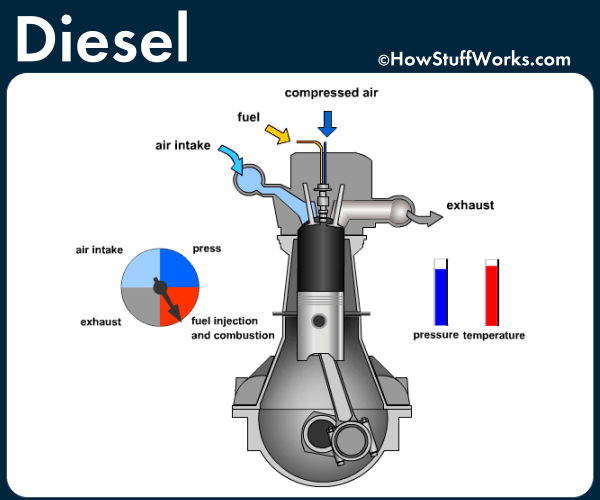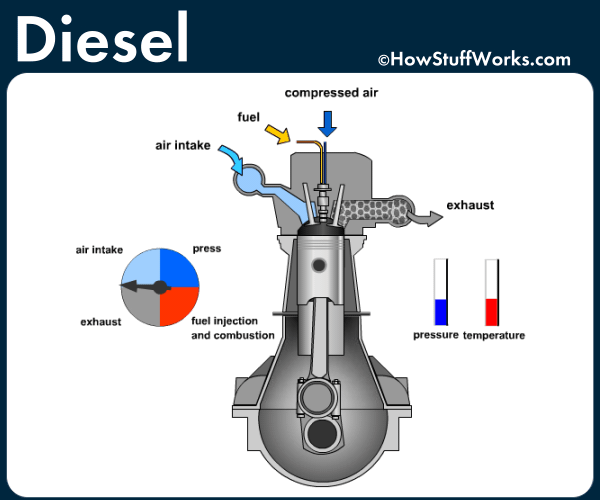
The main difference between a diesel engine and a gas powered engine is the way in which the combustion occurs.
In gas engines, the fuel combines with air and then compresses by the piston head and ignites with a spark plug. This combusts the fuel and force the piston back down. This process is outlined by the four-stroke combustion cycle.
The initial stroke, known as the intake stroke pulls air into the cylinder. The compression stroke constricts the air and injects fuel, causing combustion. This combustion leads to the power stroke, forcing the piston down from the and rotating the crank shaft. Lastly, the exhaust stroke resets the cycle by bringing the piston to the top of the cylinder and discharging exhaust gasses.
In a diesel engine, a similar four-stroke cycle follows, albeit with a several major changes. In the compression stage air is compressed before the fuel is added and through a process called auto ignition, the diesel fuel combusts due to the high temperature of the compressed air in the cylinder without the need of a spark. Glow plugs replace spark plugs in diesel engines and are only used for the initial combustion.

Maintenance and Repair
When it comes to maintenance, gas engines are typically cheaper to maintain and repair than their diesel counterpart. Gas engine assemblies use smaller components than diesel engines requiring much less lubrication or in the case of engines, oil. Both types of engines require careful disassembly and precision re-assembly. Bolts must fasten via a high-quality torque wrench as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Due to the amount of oil needed and that is being used for the lower torque application of diesel engines, the maintenance costs add up. Other than oil, the spark plugs in a gas engine should be replaced about every 50,000 miles to ensure proper combustion. Glow plugs in a diesel engine require replacement every 100,000 miles.
In terms of the lifespan of the engines, the replaceable liner in a diesel engine allows for maintenance and repair. In terms of general maintenance and repair, gas engines are cheaper. However, diesel engines provide much beeter longevity.

In large industrial applications, gas engines and diesel engines used in power generation typically require more frequent maintenance checks. Ensuring proper combustion, lubrication, and fuel levels are the major priorities in keeping a large combustion engine healthy. Similarly, being mindful of ideal operating temperatures and environmental factors provide important considerations for the long term health of industrial-grade engines.
Diesel vs. Gas Engine Applications and Life Expectancy
Diesel engines and gas engines vary in their applications. Typically speaking, diesel engines suit low RPM and high torque applications and subsequently towing and moving heavy loads. For this reason, a lot of heavy duty trucks come equipped with diesel engine for their towing capabilities. On the other hand, gas engines provide higher RPM and low torque. This type of application covers most other types of vehicles and accounts for most consumer commuter vehicles.

Because of their heavy-duty applications, diesel engines are designed with removable cylinder liners that may be replaced every couple hundred thousand miles. Gas engines lack the liner design. Thus, wear directly affects the casting of the motor. Because of this diesel engines are known to last far longer than their gas counterpart.

Other applications of diesel and gas engines are typically found in the area of power generation. Larger-scale diesel and gas engines may be used for large-scale electricity generation. Typically for shorter and smaller applications of power generation such as in residential areas, gas engine generators are the ideal choice as they offer quick power for short amounts of time and are usually cheaper than their diesel counterpart. However, if long term idling and power generation are required, diesel generators are ideal as they are far more robust and useful for longer-term applications.
External factors come into play when choosing between diesel and gas engines such as temperature. Due to the absence of spark plugs, starting a diesel engine in colder weather used to be a major concern, but with the introduction of glow plugs, preheating the engine to operate properly has increased the robustness of the diesel engine. Gas engines use spark plugs for combustion, making temperature less of a concern.
Other uses for diesel and gas engines include construction, mining, forestry, and agricultural applications.
When considering the low rpm applications of the diesel engine, it means that it cranks far less than the gas counterpart which also contributes to the diesel engine’s longer life span. As a rule of thumb, gas engines show a similar amount of wear at 120,000 miles that diesel engines display around 300,000 miles.