Q235 is low-carbon structural steel often used in China. This article will discuss Q235 steel, properties, equivalent grades, and applications.
Q235 Steel

“Q” is the first character of the Chinese spelling of “Qu Fu Dian,” which translates to Yield Point. While “235” refers to the minimum yield strength, 235 MPa tested with steel diameter ≤ 16mm. The Chinese standard GB/T 700 divides Q235 material into four quality grades: Q235A, Q235B, Q235C, and Q235D. It is used in production without heat treatment because it is mild steel. It has good plasticity and weldability.
Special process procedures like preheating and post-welding heat treatment are usually not necessary during welding. It has good practical performance, relatively low price, and high-cost performance.
Properties
Physical Properties of Q235 Steel
Q235 steel provides good plasticity, toughness, weldability, and one particular advantage for which it is well known: good cold bending performance.
The following list summarizes Q235 steel physical properties:
- Density: 7.85g/cm3
- Melting point: about 1493℃
- Specific heat capacity: 470J/(Kg·K) at 20 ℃
- Electrical resistivity: about 0,15 (20 ℃)
- Elastic modulus: 200 GPa (kN/mm2)
- Thermal conductivity: 53-49 (W/m·K) (0-100 ℃)
- Coefficient of thermal expansion: 1.3-11.6 (10-6/K) (20 ℃)
- Young’s modulus: 200 GPa (kN/mm2)
- Poisson’s ratio : 0.24-0.28
Mechanical Properties
The yield value of Q235 falls as the thickness of the material grows. The performance is comprehensive and adequate due to the mild carbon content.
The following list summarizes Q235 steel physical properties:
- Tensile Strength, Ultimate: 400 – 550 MPa
- Tensile Strength, Yield: 250 MPa
- Elongation at Break: 20%
- Modulus of Elasticity: 200 GPa/29000 ksi
- Compressive Yield Strength: 152 MPa/22000 psi
- Bulk Modulus: 160 GPa/23200 ksi
- Poissons Ratio: 0.26/0.26
- Shear Modulus: 79.3 GPa/11500 ksi
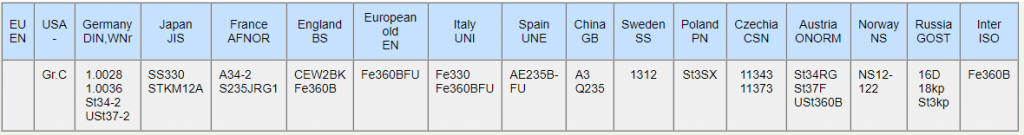
Q235 Steel Equivalent Grades
Q235 steel can be substituted with equivalent materials that include A36 USA ASTM, S235JR, and SS400 Japanese JIS.
A36 USA ASTM

ASTM A36 Steel plate equivalent grade is Q235B in China. The two equivalent steel grades share much in common yet there are discernable differences. Major differences between A36 and Q235B are as follows:
- Yield Point: (A36=250MPa, Q235B=235MPa)
- Tensile Strength: (A36=400-550MPa, Q235B=375-500MPa)
- Different element content requirements:
- A36: C =< 0.25%, Si is less than or equal to 0.4%, P < 0.04%, s is less than or equal to 0.05%;
- Q235B:C=0.12-0.2%, Si is less than or equal to 0.3, P < 0.045%, s is equal to or less than 0.045%).
- Q235 manganese content (Mn) = 0.30-0.70% while A36 does not require manganese.
S235JR

S235JR carbon steel plate provides the European standard for non-alloy structural steel. Its equivalent to GB Q235 steel plates and its use centers on structural steels used for welding, bolting, and riveted structures. Part 2 of the EN 10025 specification applies. The “S” denotes structural steel, while 235 means the steel possesses a yield strength of 235 MPa. The ‘JR’ mark shows the material passed a Charpy V-notch impact test at 27 joules at room temperature.
SS400

SS400 provides a similar formulation to China’s Q235. However, there are distinctions in specific indicators. For example, Q235 contains a chemical composition of C, Si, Mn, S, and P, but SS400 only provides S, and P in quantities less than 0.050%.
Q235 provides a yield strength greater than 235MPa, while SS400’s yield strength rates at 245MPa. SS400 has an equivalent standard number in the Japanese system of steel marking known as JIS G3101.
Because the carbon content is moderate, it provides generally good all-around performance. Strength, plasticity, and weldability, and general properties allow for flexible and demanding service.
More worldwide equivalent grades are listed below:
Applications
Not only does Q235 have exceptional toughness, weldability, and plasticity, but it provides strength in cold bending applications. It’s ideal for welded structures, including factory structures, steel bars, towers, boilers, bridges, containers, and automobiles. Many structural skids fabricate from Q235, although A36 sees more common use, particularly in the US and specification-heavy applications.
Other mechanical items made of Q235 include stands, stressed rods, nuts, connecting rods, and brackets. Distributors typically provide steel plates and beams of Q235 in pre-cut lengths. Fabricators then further process the steel to meet project and customer specifications.




