Stud bolts are essentially threaded bars that mainly connect flanges. When coupled with suitable nuts, stud bolts can also mechanically fasten any parts together. Drilling, pipeline, and even general industry and refinery of petrochemical use these bolts.
This article covers the types of stud bolts, the stud bolt size chart, and their use in anchor applications.

Types of Stud Bolts
Stud bolts fasten loads and disseminate stresses. They reduce the occurrence of breakages and damage. Depending upon their design and threading patterns, there are different types of stud bolts. The list of stud bolts types includes many variations:
- Fully Threaded
- Tap End
- Double End
- Bonding Stud
- Weld Bolt
- Dowel Screw
- Clinch Stud
Fully Threaded

This type of fastener presents as a long threaded bar. The fully threaded stud uses nuts at each end to fasten large parts together. This stud also serves as an adjustable part of machines and structures. With this, nuts can move a fair distance while drawing on a large force. These studs are commonly used with objects that require quick assembly and disassembly.
Tap-End

This second type is typically short in length. Tap-ends purposefully rivet into a punctured hole. They also have a shaft and a long thread designed to accept a nut. The size of the stud measures overall. The tap end has a chamfered point, but the nut end may have a chamfered or round point at the manufacturer’s option. Tap end studs are special stud bolts that require custom bolting requirements.
Double-End

The double-end variation provides equal-length threads on both ends with a shaft in the middle. The threads accommodate nuts and conform to Class 2A tolerances. These fasteners find frequent use in machine and automotive applications.
Bonding stud
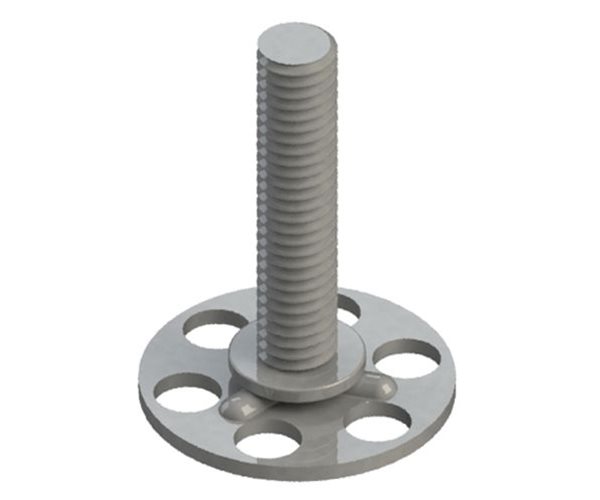

The bonding stud is an outright flat and wide-headed thread with holes in the head. In addition, it works as a bond into joint and composite parts providing an immovably attached stud.
Bonding fasteners provide a solid metal anchor point on even difficult-shaped structures made of various materials, including plastic, carbon fiber, and fixing issues for GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) products. Still, they’ve also found several other applications where traditional fasteners fall short.
They can either glue into the substrate or surface-mount to most materials using adhesives or mechanical fasteners like screws, rivets, or nails. A stud or female thread welds to a perforated base plate. Bonding fasteners provide load-distributing anchorage points, thus reducing the risk of break-through on thin-wall structures.
Weld Bolt
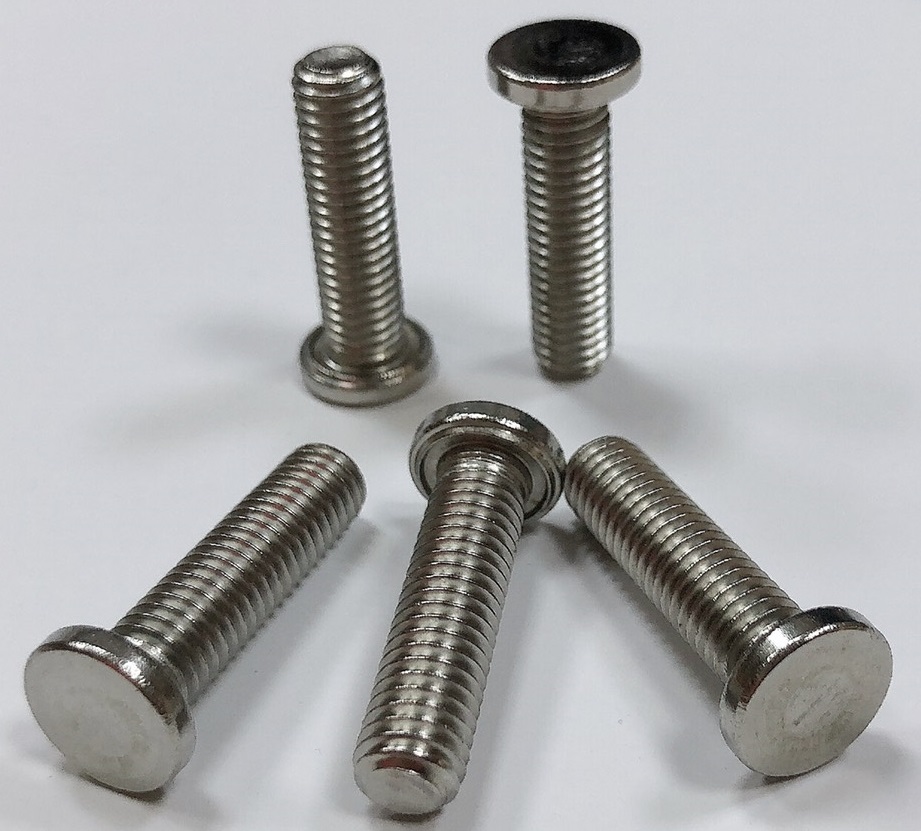

This type of bolt has a standard-length machine thread. Its thin wide tip design specifically makes it easy to weld. Weld bolts provide a steadfast bond and fabricators frequently use this type of connection. Weld fasteners allow one side of the connection to be securely fastened to the base material.
Dowel Screw

The dowel screws into either wood or metal. While wood connections drill directly into the subject material, metal applications affix into a socket. The most frequent applications are ones of little interest to fabricators such as furniture building and attaching balusters to staircases and flooring. Whether a wood or metal application, these fasteners require installation with locking pliers or a driver tool.
Clinch Stud
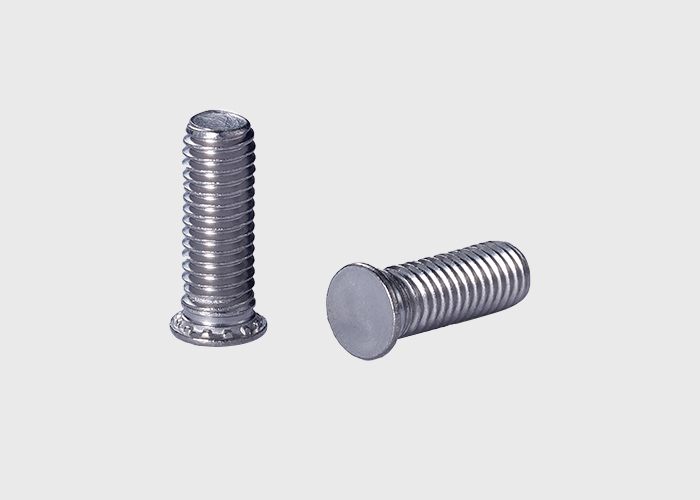

The last type swages its small thin head into sheet metal notches. Clinch studs secure their head to the mating material while also providing strong torque resistance. The real benefit of a clinch stud is that it eliminates welding.
Stud Bolt Size Chart
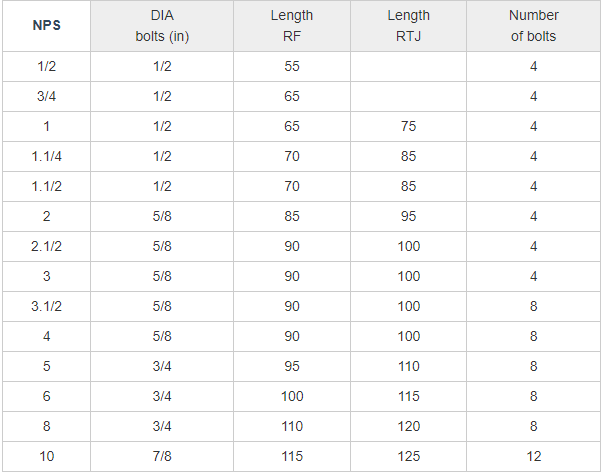
Stud bolt length is commonly measured end to end or first thread to first thread. The initial thread is defined as the junction of the thread’s primary diameter and the point’s base.
General notes for the length dimensional tolerances for all stud bolts:
- Length to 12 inch tolerance = ± 1.6 mm
- Length over 12 inch to 18 inch tolerance = ± 3.2 mm
- Length over 18 inch tolerance = ± 6.4 mm
- The length of the Stud Bolt does not include the height of the chamfers (points).
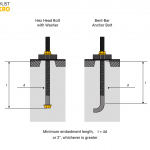
Stud Anchor Bolt
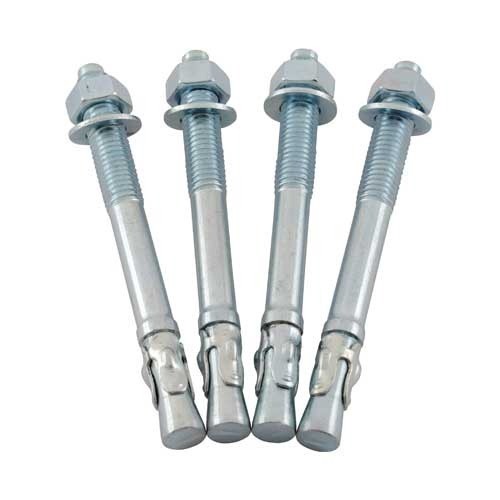

A stud concrete anchor bolt is a concrete anchor that has a threaded section jutting out from the concrete once put into the concrete. Standard carbon steel, zinc plated or hot-dipped galvanized, makes stud concrete anchor bolts.
They require a pre-drilled hole with the same diameter as the anchor. Hammer driving the anchor causes the expander plug to expand, thus eliminating torquing requirements. This bottom load-bearing design is helpful in leveling and jacking applications.